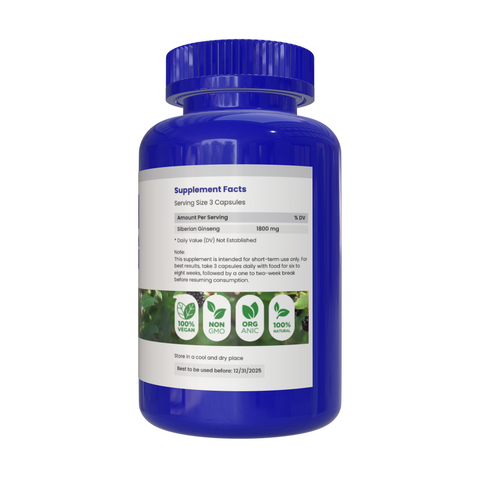
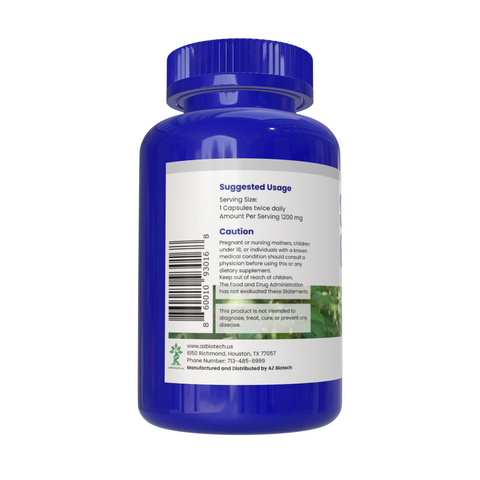
Siberian Ginseng
Siberian ginseng was traditionally used to prevent colds and flu and to increase energy, longevity, and vitality. It is widely used in Russia as an "adaptogen." An adaptogen is a substance that is supposed to help the body better cope with either mental or physical stress.
Siberian ginseng (Eleutherococcus senticosus), also known as eleuthero, has been used for centuries in Eastern countries, including China and Russia. Despite its name, it is completely different from American (Panax quinquefolius) and Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng) and has different active chemical components. The active ingredients in Siberian ginseng, called Eleutherosides, may stimulate the immune system.
Until recently, most scientific research on Siberian ginseng was done in Russia. Research on Siberian ginseng has included studies on the following:
HERPES VIRAL INFECTION
One double-blind study of 93 people with herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 2, which can cause genital herpes, found that taking Siberian ginseng reduced the number of outbreaks. Outbreaks that did happen were less severe and did not last as long. Talk to your doctor about whether using Siberian ginseng to help prevent herpes outbreaks would help.
PHYSICAL PERFORMANCE
Siberian ginseng is often said to improve athletic performance and increase muscle strength. While some studies have found positive results, others have found that Siberian ginseng had no effect.
MENTAL PERFORMANCE
Siberian ginseng is often used to increase mental alertness. However, there have not been enough scientific studies to show that it really works. One preliminary study found that middle-aged volunteers who took Siberian ginseng improved their memory compared to those who took a placebo.
QUALITY OF LIFE
One study found that elderly people who took Siberian ginseng had better mental health and social functioning after 4 weeks of therapy, compared to those who took a placebo. But after 8 weeks, the benefits started to dissipate.
COLDS AND FLU
Some double-blind studies have found that a specific product containing Siberian ginseng and Andrographis reduced the severity and length of colds when taken within 72 hours of symptoms starting. Researchers do not know whether Siberian ginseng was responsible or whether it was andrographis, or the combination of the two herbs.
One study compared the same product with amantadine, a drug used to treat some kinds of flu. People with flu who took the same product saw their symptoms go away faster than those who took amantadine.
Another study found that healthy people who took Siberian ginseng for 4 weeks had more T-cells, which may indicate their immune systems were stronger.
What is it Made Of?
Siberian ginseng supplements are made from the root. The root has a mixture of components called Eleutherosides that are thought to have health benefits. Among the other ingredients are chemicals called polysaccharides, which have been found to boost the immune system and lower blood sugar levels in animal tests.
Available Forms
Siberian ginseng is available as liquid extracts, solid extracts, powders, capsules, and tablets, and as dried or cut root for tea.
The quality of many herbal supplements, including Siberian ginseng, may vary greatly. Tests of commercial products claiming to contain Siberian ginseng found that as many as 25% had none of the herbs. Plus, many were contaminated with contents not marked on the label. Purchase Siberian ginseng and all herbal products from reputable manufacturers. Ask your pharmacist for help.
How to Take It
DO NOT give Siberian ginseng to a child.
For adult use, Siberian ginseng comes in many forms and is often combined with other herbs and supplements for such things as fatigue and alertness. To find the right dose for you, talk to an experienced healthcare provider.
For chronic conditions, such as fatigue or stress, Siberian ginseng can be taken for 3 months, followed by 3 to 4 weeks off. DO NOT take Siberian ginseng without your doctor's supervision.
Precautions
The use of herbs is a time-honored approach to strengthening the body and treating disease. Herbs, however, have components that can trigger side effects and interact with other herbs, supplements, or medications. For these reasons, herbs should be taken with care, under the supervision of a health care provider qualified in the field of botanical medicine.
Siberian ginseng is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, people with high blood pressure, sleep apnea, narcolepsy, heart disease, mental illness such as mania or schizophrenia, women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, and people with autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or Crohn's disease, should not take Siberian ginseng.
Women who have a history of estrogen-sensitive cancers or uterine fibroids should ask their provider before taking Siberian ginseng because it may act like estrogen in the body.
Some side effects may include:
- Confusion
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Insomnia
- Irregular heart rhythm
- Nosebleed
- Vomiting
Possible Interactions
If you are being treated with any of the following medications, you should not use Siberian ginseng without first talking to your healthcare provider:
Anticoagulants (blood thinners)
Siberian ginseng may increase the risk of bleeding, especially if you already take blood thinners such as aspirin, warfarin (Coumadin), or clopidogrel (Plavix).
Corticosteroids (such as prednisone)
Siberian ginseng may interact with steroids.
Digoxin
Siberian ginseng may raise blood levels of digoxin, a medication used to treat heart conditions. This can increase the risk of side effects.
Diabetes medications
Siberian ginseng may lower blood sugar levels, raising the risk of hypoglycemia or low blood sugar.
Lithium
Siberian ginseng could make it harder for the body to eliminate lithium, meaning dangerously high levels could build up.
Other medications
Siberian ginseng may interact with medications that are broken down by the liver. If you take these medications, ask your doctor before taking Siberian ginseng.
Drugs that suppress the immune system
Siberian ginseng may boost the immune system and may interact with drugs taken to treat an autoimmune disease or drugs taken after an organ transplant.
SedativesSiberian ginseng may make the effects of sedatives stronger, especially barbiturates. Barbiturates are medications, including pentobarbital, that are used to treat insomnia or seizures